NCERT Solutions for Class-9 Science Chapter-1 Matter in Our Surroundings
NCERT TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS
Question 1. Which of the following are matter ?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold drink, smell of perfume.
Answer: Chair, air, smell, almonds, cold drink, smell of perfume are matter. Please note that the smell whether pleasant or foul is due to the presence of some particles in air. It is therefore, a matter. Love, hate, thought and cold are simply feeling. They do not represent matter.
Question 2. The smell of hot sizzling food reaches us several metres away. However, it is not so in case the food is cold. Explain.
Answer: When food is sizzling hot, it releases the vapours of its contents. Since the kinetic energy of the particles is very high in the vapour state, these particles readily mix up with the particles of air. They can reach us even at a distance of several metres. However, when the food is cold, the vapours released will be comparatively less. Moreover, their kinetic energy is also very small. Under these conditions, one has to come quite close in order to smell the contents of the food.
(CBSE 2013)
Answer: The observation explains the following properties of water (liquid state of matter) or any other liquid.
1. The inter particle forces of attraction are not very strong in water.
2. The inter particle spaces are somewhat large in water.
3. All these properties associated with the liquid state or water enable the diver to cut through water in a swimming pool.
Answer: Characteristics of the Particles of Matter,
Matter is composed by particles and there are interparticle spaces as well. Let us brief by study the main characteristics of these particles supported by some activities.
1. Particle Size is Extremely Small
2. Particles are in a State of Motion
3. Inter Particle Attractions Keep Particles Close
4. Effect of Temperature on Particle Motion
Question 5. The mass per unit volume of a substance is known as density (density = mass/volume). Arrange the following in order of increasing density :
Air, exhaust from chimneys, honey, water, chalk, cotton and iron.
Answer: The increasing order of density for the given substances is :
Air, exhaust from chimneys, cotton, water, honey, chalk, iron.
Actually, the density of a substance depends upon the number of particles per unit volume as well as upon their mass. The number of the particles is related to their size as well as the attractive forces among them. Keeping this in view, the increasing order of density is as given above.
Question 6. Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of the three states of matter.
Answer: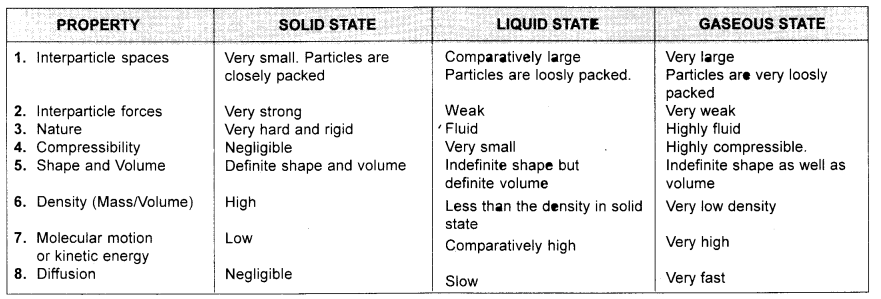
rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling of a gas in cylinder, shape, kinetic enegy and density.
Answer:
Rigidity: Solids are known for their hardness and rigid nature.
Compressibility: Actually, the constituent particles are so closely packed in a solid that they either do not come closer or do so only slightly when a high pressure is applied. However, there are some exceptions. For example, a sponge made from some foam or rubber material can be easily compressed.
Fluidity: We have seen that rigidity is maximum in the solid state and fluidity or particle motion is negligible. In the liquid state of a substance, both these characters are different. The liquids are less rigid than the solids and the molecular motion is also comparatively more.
Filling of a Gas in Cylinder: All of us are quite familiar with a cooking gas cylinder which contains in it liquefied petroleum gas, often called L.P.G. It is a mixture of different gases such as propane, butane etc. These are so highly compressed that they are in the liquefied form. When the regulator is opened, the liquid escapes from the nozzle of the cylinder into a space where pressure is very less.
Shape: Solids generally have fixed shapes. They donot change their shapes even when put in different containers. For example, blue crystals of copper sulphate have needle like shape which they retain whether kept in a beaker or in a china dish or placed on the palm of our hand.
Kinetic Enegy: The kinetic energy of the particles in the liquid state of a substance is more than in solid state. It further increases with the rise in temperature.
Density: The density of the gas (mass/volume) is very small and the gases are therefore, light.
Question 8. Why does a gas fill completely the vessel in which it is kept ?
Answer: This happens because of fast diffusion of the particles in a gas. The number of vacant spaces or voids in the gaseous state is very large. This means that the particles of a gas move at a very fast speed. They readily fill completely the vessel in which the gas is kept. Thus, the volume of the gas is the same as that of the vessel.
Question 9. A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container. Assign reason. (CBSE 2012, 2013)
Answer: The molecules in a gas have large kinetic energy. They strike the walls of the container with certain force and impart momentum to them. The force per unit area or momentum is responsible for the pressure of the gas.
Answer: A wooden table should be called a solid because it matches the characteristics of the solid state. For example,
1. It is very hard and rigid.
2. Its shape cannot be changed by altering temperature or pressure. .
3. It is quite heavy which means high density.
4. There is no movement of the constituent particles present.
Question 11. We can easily move our hand in air but to do so the same through a solid block of wood, we need a ‘Karate expert’. Explain.
Answer: In air, the interparticle spaces are very large in number and the interparticle forces are quite weak. These can be easily overcome. That is why our hand can move in air. These spaces help in moving our hand in air, But in a solid block, the constituent particles are quite close and the interparticle forces are very strong. In case, one has to move his hand through a solid, it will be extremely difficult. Only a karate expert may do so.
Question 12. Liquids generally have low density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why ?
Answer: Ice (solid state) is expected to be heavier than water (liquid state). But it is lighter and floats over water. Actually, ice has a cage like structure which means that vacant spaces are left when H2O molecules are linked in ice. The number of these spaces are comparatively less in water. In other words, we can also say that the structure of ice is more porous than that of water. Therefore, water is dense as compared to ice or ice floats over water.
Question 13. Convert the following temperatures to Celsius scale :
(a) 300 K
(b) 573 K.
Answer:
(a) (300 – 273) = 27°C
(b) (573 – 273) = 300°C.
Question 14. What is the physical state of water at : (a) 250°C (b) 100°C ?
Answer: Boiling point temperature of water is 100°C. Above this temperature (250°C), water exists in the gaseous state i.e., as vapours or as steam. However, at 100°C, both liquid and gaseous states are present. Actually, at the boiling point temperature, both the liquid and gaseous states of a substance co-exist. These are in a state of equilibrium. We may conclude that at 100°C, both liquid water and vapours are present but at 250°C we have only vapours or steam and no liquid.
Question 15. For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state ?
Answer: Once the change of state of a substance begins or starts, the energy which is now supplied is being used up as latent heat. It means that it does not increase the kinetic energy of the particles and is used up only to overcome the inter-particle forces in that particular state and to bring about a change in state. Therefore, the temperature becomes constant.
Question 16. Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Answer: In order to liquefy a gas, the constituent particles or molecules have to be brought closer. The atmospheric gases can be liquefied either by increasing pressure or by decreasing temperature.
Question 17. A cooler is quite effective on a hot and dry day. Explain.
Answer: Under the conditions, the humidity level in the atmosphere is quite low and the evaporation rate of water is expected to be high. Since cooling is caused during evaporation, the air which escapes from the cooler is compartively cold under these conditions. Therefore, is quite effective on a hot and dry day.
Question 18. How does water kept in an earthen pot become quite cold during summer ?
Answer: The earthen pot is full of small pores. Water present in these pores has a tendency to escape at a fast rate during summer. The escaping molecules of water appear as water vapours and evaporate. Since cooling is caused in evaporation, the temperature of the water inside the earthen pot gets considerably lowered and it becomes cold.
Question 19. When we pour some acetone or perfume on our palm, we get a cooling sensation. Assign reason.
Answer: Both acetone and perfume are low boiling liquids. When any of them is poured on the palm, it readily changes into vapours or evaporates. For this, it needs some energy which is taken from the palm. The temperature of the palm gets lowered and we get a cooling sensation.
Question 20. Why can we sip hot tea from a saucer faster than from a cup ?
Answer: The phenomenon of change of liquid to the vapour state at any temperature below the boiling point of the liquid.
In a liquid, the particles or molecules experience mutual forces of attraction. However, these are not stationary and have some kinetic energy at all temperatures. The particles of a liquid are also colliding with one another and exchanging energy during the collisions. Above the liquid surface, atmosphere or air is present which is a mixture of several gases. The particles of the liquid present on the surface have a tendency to come out from the surface so that they may acquire more freedom to move and become part of the atmosphere. This is also known as randomness. To overcome the interparticle forces of attraction, they need some energy which they take up from the rest of the particles or molecules of the liquid. As a result, their temperature gets lowered and cooling is caused.
NCERT EXERCISE
Question 1. Convert the following temperatures to Celsius scale ?
(a) 293 K
(b) 470 K.
Answer:
(a) (293 – 273) = 20°C
(b) (470 – 273) = 197°C
Question 2. Convert the following temperatures to Kelvin scale
(a) 25°C
(b) 373°C. (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
(a) (25 + 273) = 298 K
(b) (373 + 273)’= 646 K.
Question 3. Give reasons for the following observations :
(a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid (CBSE 2011, 2013)
(b) We can get the smell of perfume sitting several metres away. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
(a) Naphthalene has a tendency to sublime i.e. it changes directly to the gaseous state. Therefore, the size of the naphthalene balls slowly decreases and ultimately they disappear. No solid residue is left.
(b) A perfume is actually a mixture of number of pleasant smelling vapours. They diffuse quite fast and can reach a person who may be even at several metres away from a person who has used perfume.
Question 4. Arrange the following substances in increasing order of attraction between the particles : water, sugar, oxygen.
(CBSE 2012)
Answer: The three substances differ in their physical state at normal temperature. Oxygen is a gas, water a liquid while sugar is a crystalline solid. Keeping this is mind, the increasing order of attraction between the particles is : oxygen < water < sugar.
(a) 25°C (b) 0°C (c) 100°C ? [CBSE 2014]
Answer:
(a) At 25°C, water is in the liquid state
(b) At 0°C, water can exist both in the solid state (ice) and in liquid state. This temperature represents the melting point of ice and freezing point of water
(c) At 100°C, water can be present both in the liquid and vapour states. This temperature corresponds to the boiling point of water and liquefication temperature of steam.
1. water at room temperature is a liquid
2. an iron almirah is a solid at room temperature. (CBSE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
1. Water is a liquid at room temperature (25°C) due to the following reasons :
2. (a) When placed in a beaker, its level cannot be changed on pressing.
(b) It can take the shape of any container in which it is placed.
(c) An iron almirah is a solid due to following reasons :
(d) Its shape does not change when pressed. This means that it is hard and rigid.
(e) It is very heavy. This means that its density is very high.
Question 7. Ice at 273 K causes more cooling than water at the same temperature. Explain. (CBSE 2015)
Answer: Ice (solid state) has extra energy in the form of latent heat of fusion (335 kj kg-1) as compared to water. When ice is to melt, it takes energy from the surroundings to overcome this latent heat. The temperature of the surroundings gets lowered or cooling is caused. Since water is already in the liquid state, it will hardly take up any energy from the surroundings.
Question 8. Why does steam produce more severe burns on the skin as compared to boiling water ? (CBSE 2015)
Answer: Steam is formed when water at its boiling point temperature of 100°C (373 K) absorbs latent heat of vaporisation. Therefore, steam has more energy than boiling water. On account of this, steam produces more severe burns on the skin as compared to boiling water.
Question 9. Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing change of state. (CBSE 2015)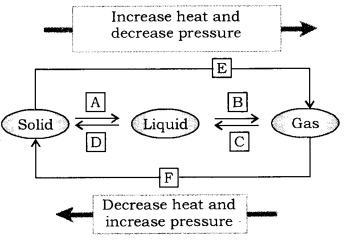
Answer:
[A] = Fusion(melting), [B]=Vaporisation , [C] = Condensation(Liquefaction),
[D] = Solidification, [E] = (freezing), Sublimation, [F] = Solidification of gaseous state.

0 comment
Post a Comment