NCERT Solutions for Class-6 Science Chapter-13 Fun with Magnets
(a) Artificial magnets are made in different shapes such as ______, ______ and ______.
(b) The materials which are attracted towards the magnet are called ______.
(c) Paper is not a ______ material.
(d) In the olden day’s sailors used to find direction by suspending a piece of ______.
(e) A magnet always has ______ poles.
Answer:
(a) 1. U-shaped
2. Cylindrical
3. Base shaped
(b) Magnetic
(c) Magnetic
(d) Magnet
(e) Two
(i) A cylindrical magnet has only one pole.
(ii) Artificial magnets were discovered in Greece.
(iii) Similar poles of a magnet repel each other.
(iv) Maximum iron filings stick in the middle of a bar magnet when it is brought near them.
(v) Bar magnets always point towards North-South direction.
(vi) A compass can be used to find East-West direction at any place.
(vii) Rubber is a magnetic material.
Answer:
(i) False
(ii) True
(iii) True
(iv) False
(v) True
(vi) False
(vii) False
Question 3. It was observed that a pencil sharpener gets attracted by both the poles of a magnet although its body is made of plastic. Name a material that might have been used to make some part of it.
Answer: Iron might have been used to make some part of a pencil sharpener.
Question 4. Column I shows different positions in which one pole of a magnet is placed near that of the other. Column II indicates the resulting action between them for each situation. Fill in the blanks.
| Column I | Column II |
| N-N | ……………… |
| N-….. | Attraction |
| S-N | ………………. |
| …..-S | Repulsion |
Answer:
| Position of two magnets | Behavior |
| N-N | Repulsion |
| N-S | Attraction |
| S-N | Attraction |
| S-S | Repulsion |
Answer: Properties of a magnet are:
1. The magnet has two poles-north poles and a south pole.
2. Same poles repel each other and different poles attract each other.
Question 6. Where are the poles of a bar magnet located?
Answer: Poles of a bar magnet are located at the ends.
When a bar magnet is placed near some iron filings, we observe more iron filings clinging to the magnet near its ends.
See Figs. 13.3 and 13.4(a).
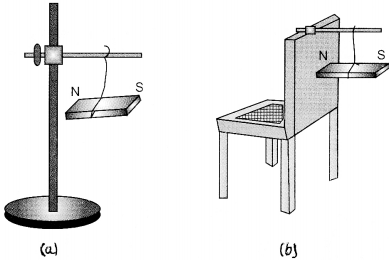
The ends of a magnet where maximum iron filings get clung, i.e., the attraction is strongest, are known as poles.
Question 7. A bar magnet has no markings to indicate its poles. How would you find out near which end is its north pole located?
Answer: We will suspend the bar magnet. It will come to rest in a north-south direction. The end of the magnet pointing towards the north direction is called a north pole.
Question 8. You are given an iron strip. How will you make it into a magnet?
Answer: We can convert an iron strip by repeatedly stroking it by a bar magnet systematically. Take the iron strip and keep it on a wooden table. Stroke it with one pole of a bar magnet in one direction. When you reach the other end of the iron strip, lift the magnet and bring the same pole back to the starting end of the iron piece, stroke again, in the same direction. Repeat this process about 30-40 times. After that check the iron strip whether the iron strip has now become a magnet. If not, continue the process for some more time. Remember the pole of the magnet and the direction of stroking is not to be changed. In the same way, the iron needle can also be converted into a magnet.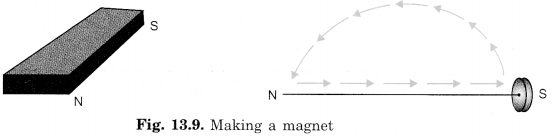
Question 9. How is a compass used to find directions?
Answer: The compass is kept at the place where we want to know the directions. Its needle indicates the north-south direction when it comes to rest. The compass is then rotated until the north and south marked on the dial are at the two ends of the needle. Thus north and south directions are identified.
Question 10. A magnet was brought from different directions towards a toy boat that has been floating in water in a tub. The effect observed in each case is stated in Column I. Possible reasons for the observed effects are mentioned in Column II. Match the statements given in Column I with those in Column II,
| Column I | Column II |
| Boat gets attracted towards the magnet | Boat is fitted with a magnet with north pole towards its head |
| Boat is not affected by the magnet | Boat is fitted with a magnet with south pole towards its head |
| Boat moves towards the magnet if north pole of the magnet is brought near its head | Boat has a small magnet fixed along its length |
| Boat moves away from the magnet when north pole is brought near its head | Boat is made of magnetic material |
| Boat floats without changing its direction | Boat is made up of non-magnetic material |
Answer :
| Column I | Column II |
| Boat gets attracted towards the magnet | Boat is made up of magnetic material |
| Boat is not affected by the magnet | Boat is made up of non-magnetic material |
| Boat moves towards the magnet if north pole of the magnet is brought near its head | Boat is fitted with a magnet with south pole towards its head |
| Boat moves away from the magnet when north pole is brought near its head | Boat is fitted with a magnet with a north pole towards its head |
| Boat floats without changing its direction | Boat has a small magnet fixed along its length |

0 comment
Post a Comment