NCERT Solutions for Class-7 Science Chapter-1 Nutrition in Plants
Answer: Organisms need to take food to,
1. get the energy to do work.
2. build up the body.
3. repair damages in the body.
4. maintain the functions of the body.
Question 2. Distinguish between a parasite and a saprotroph.
Answer:
| Parasite | Saprotroph |
1. A parasite takes the food from the organism on which it survives. | 1. They secrete digestive juices on the dead and decaying matter and convert it into a solution. |
| 2. They feed on a living organism. | 2. They feed on dead and decaying matter. |
| 3. The organism on which it survives is called host. | 3. They do not feed on a living organism. |
| 4. It deprives the host of valuable nutrients. | 4. There is no host at all. |
Answer:
1. Take two healthy green potted plants of the same kind in order to remove all the starch from the leaves.
2. Keep one in the darkroom (or in a black box) for 72 hours and the other in the sunlight.
3. Now, take one leaf from each of the plants.
4. Put few drops of iodine solution on each of the leaves.
5. The leaf kept in the sunlight will turn blue-black due to the presence of starch.
6. The leaf kept in the dark will not turn blue-black because of the absence of starch.
Question 4. Give a brief description of the process of synthesis of food in green plants.
Answer: The leaves of a plant have a green pigment called chlorophyll. In the presence of sunlight, they use carbon dioxide and water to synthesize carbohydrates.
Carbon dioxide + Water ---------------> Carbohydrade + Water + Oxygen
During the process, oxygen is released. The carbohydrates ultimately get converted into starch.
Carbon dioxide from the air is taken through stomata. Water and minerals are absorbed by the roots and transported to the leaves.
Question 5. Show with the help of a sketch that plants are the ultimate source of food.
Answer: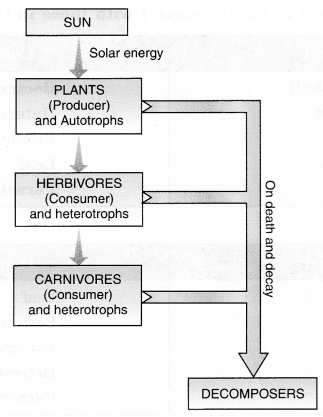
Plants capture solar energy by a unique process called photosynthesis.
1. Green plants are called …….. since they synthesize their own food.
2. The food synthesized by the plants is stored as ………
3. In photosynthesis solar energy is captured by the pigment called ……….
4. During photosynthesis plants take in ……… and release ……….
Answer:
1. autotrophs
2. starch
3. chlorophyll
4. carbon dioxide, oxygen
1. A parasitic plant with a yellow, slender, and branched stem.
2. A plant that is partially autotrophic.
3. The pores through which leave exchange gases.
Answer:
1. Cuscuta
2. Insectivorous plants
3. Stomata
(a) Amarbel is an example of:
(i) Autotroph
(ii) Parasite
(iii) Saprotroph
(iv) Host
(b) The plant which traps and feeds on insects is:
(i) Cuscuta
(ii) China rose
(iii) Pitcher plant
(iv) Rose
Answer:
(a) (ii) Parasite
(b) (iii) Pitcher plant
Question 9. Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| Chlorophyll | Bacteria |
| Nitrogen | Heterotrophs |
| Cuscuta | Pitcher plant |
| Animals | Leaf |
| Insects | Parasite |
Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| Chlorophyll | Leaf |
| Nitrogen | Bacteria |
| Cuscuta | Parasite |
| Animals | Heterotrophs |
| Insects | Pitcher plant |
(i) Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis. (T/F)
(ii) Plants which synthesize their food are called saprotrophs. (T/F)
(iii) The product of photosynthesis is not a protein. (T/F)
(iv) Solar energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis. (T/F)
Answer:
(i) F
(ii) F
(iii) T
(iv) T
Question 11. Choose the correct option from the following:
Which part of the plant takes in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis?
(i) Root hair
(ii) Stomata
(iii) Leaf veins
(iv) Petals
Answer:
(ii) Stomata
Question 12. Choose the correct option from the following:
Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mainly through their:
(i) roots
(ii) stem
(iii) flowers
(iv) leaves
Answer:
(iv) leaves
Question 13. Why do farmers grow many fruits and vegetable crops inside large greenhouses? What are the advantages to the farmers?
Answer: Most of the crops require a lot of nitrogen to make protein. After the harvest, the soil becomes deficient in nitrogen. Though nitrogen gas is available in the air, plants cannot use it directly. They need nitrogen in a soluble form. The bacterium called Rhizobium can take atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into soluble nitrogenous components. Rhizobium is present in the roots of some fruits and vegetables and legumes plants which provides nitrogen to them. By crop rotation, farmers increase the nitrogenous compounds in soil. So there is no need to add nitrogenous fertilizers to the soil in which leguminous plants are grown. By this practice, farmers provide good quality crops and save money.

0 comment
Post a Comment