NCERT Solutions for Class-9 Science Chapter-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
NCERT TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS
Question 1. Who discovered cell, and how ?
Answer: Robert Hooke (1665). He thinly pared a piece of cork and observed it under his self made primitive microscope. The scientist found that cork possesses a number of small box-like structures which he named cells (cellulae which later’abbreviated to cells). His work was published in the form of a book called Micrographia.
Question 2. Why is cell called structural and functional unit of life ?
Answer:
Structural Unit: A living organism is made up of one or more cells. Therefore, cell is structural unit of life. Functional Unit. All life functions of an organism reside in its cells. Cells may also become specialised to perform specific functions like contraction in muscle cell or impulse transmission in nerve cell. Therefore, cells are functional units of life.
Question 3. How do substances like CO2 and water move into and out of the cell ? Discuss. (CCE 2011)
Answer: CO2 moves into and out of cells by diffusion while water does it through osmosis.
Diffusion. It is movement of particles of various substances from the region of their higher concentration to the region of their lower concentration,
(i) In a respiring cell, more CO2 is produced internally. As a result its internal concentration rises. As concentration of CO2 is lower in the outside medium, CO2 passes out from cell into external medium,
(ii) In photosynthetic cell, CO2 is being consumed in photosynthesis. Its intracellular concentration is lower than outside medium. Therefore, CO2 diffuses from outside to inside of the cell. Osmosis. It is movement of water from the region of its higher concentration (pure water or dilute solution) to the region of its lower concentration (strong solution) when the two are separated by a semipermeable membrane. Plasma membrane functions as a semipermeable membrane. Cell sap functions as strong solution. Therefore, external water enters the cell (endosmosis) till wall pressure counter-balances this tendency. If the external medium has a very strong solution, water would pass out from the cell into the external medium. The phenomenon is called exosmosis.
Question 4. Why is plasma membrane called selectively permeable membrane ? (CCE 2012)
Answer: Cell membrane is semipermeable membrane for water. It permits the entry of gases through diffusion. Ions, sugar, amino acids, etc. pass through the plasma membrane by an active process. Plasma membrane is impermeable to certain other materials. Therefore, it is selectively permeable.

Answer:
2. (Left side),
(i) Poorly defined due to absence of nuclear envelope
(ii) Nucleoid.
4. (Right side),
(iv) Membrane bound cell organelles are present.
Question 6. Can you name the two organelles, we have studied that contain their own genetic material ?
Answer: Yes, Mitochondria and plasdds.
Question 7. If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen ?
Answer: Lysosome will burst to release digestive enzymes. Digestive enzymes will cause breakdown of various cellular components causing destruction of the cell.
Question 8. Why are lysosomes known as suicide bags ? (CCE 2011, 2012, 2013)
Answer: Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes against all types of organic materials. If their covering membrane breaks as it happens during injury to cell, the digestive enzymes will spill over the cell contents and digest the same. As lysosomes are organelles which on bursting can kill the cells possessing them, they are called suicide bags.
Question 9. Where are proteins synthesised inside the cell ?
Answer: Proteins are synthesized over the ribosomes.
NCERT EXERCISE
Question 1. Make a comparison to write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cells.
Answer: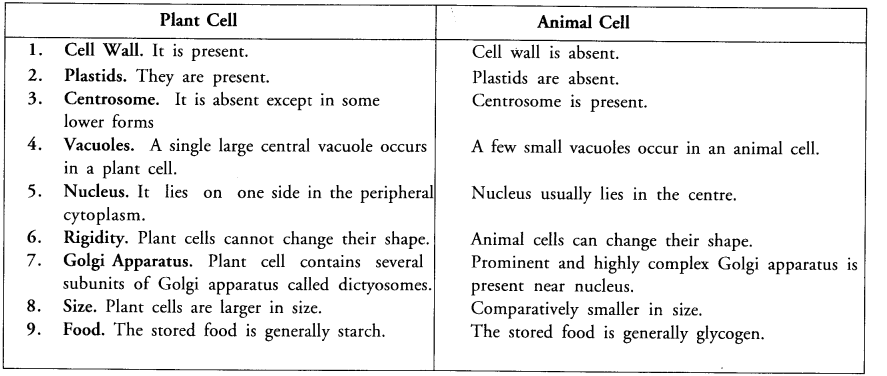
Question 2. How is prokaryotic cell different from eukaryotic cell ?
Answer: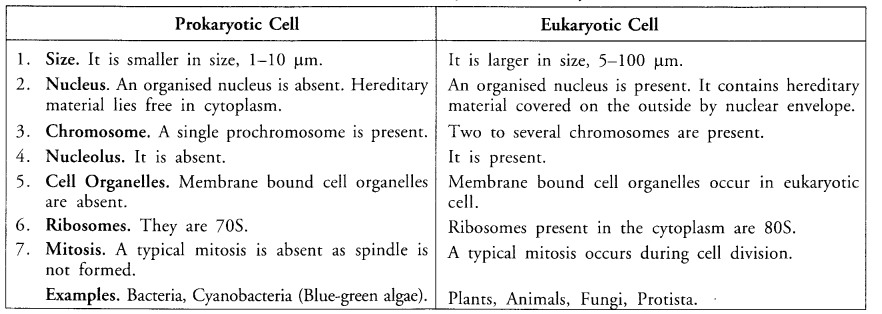
Question 3. What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down ?
Answer: There will be spilling of cytoplasm and cell organelles, bursting of lysosomes and digestion of cellular contents.
Question 4. What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus ? (CCE 2011)
Answer: There would not be any lysosome for intracellular digestion and cleansing, no complexing of molecules, no excretion and no formation of new plasma membrane.
Question 5. Which organelle is known as power house of the cell ? Why ? (CCE 2011, 2013)
Answer: Mitochondrion is known as power house of the cell because it produces most of the molecules of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) which are required for providing energy for synthesis of new chemicals, mechanical and other cellular functions.
Question 6. Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised ?
Answer: Proteins are synthesised over ribosomes of RER while lipids are synthesised over SER.
Question 7. How does Amoeba obtain food ?
Answer: Plasma membrane of Amoeba is flexible. With its help, Amoeba engulfs food particle. The engulfed food particle passes into the body of Amoeba as a phagosome. Phagosome combines with lysosome to produce digestive or food vacuole. Digestion occurs in food vacuole. The digested food passes into surrounding cytoplasm. The undigested matter is thrown out of the cell in exocytosis.
Question 8. What is osmosis ?
Answer: Osmosis is diffusion of water from the region of its higher concentration (pure water or dilute solution) to the region of its lower concentration (strong solution) through a semipermeable membrane.
Question 9. Carry out the following osmosis experiment.
Take four peeled potato halves and hollow each one out to make potato cups. One of these potato cups should be made from the boiled potato. Put each potato cup in the trough containing water. Now
(a) Keep cup A empty,
(b) Put one tea spoon sugar in cup B.
(c) Put one tea spoon of salt in cup C.
(d) Put one tea spoon sugar in boiled cup D.
Keep this set up for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following :
(i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment ?
(iii) Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed out portion of A and D.
Answer:
(i) Sugar and salt increases osmotic concentration which results in passage of water osmotically from the trough through the cells of potato B and C into its cavity.
(ii) Potato A functions as control experiment which indicates that the cavity of potato does not induce movement of water. Water does not gather in the hollowed out portion of A because it does not have a higher osmotic concentration than the cells of potato tuber.
(iii) Potato tuber D does not have living cells. Osmosis does not occur in dead cells. Therefore, despite presence of sugar in the cavity of D, no water passes from trough through dead potato cells into cavity of the tuber.

0 comment
Post a Comment