NCERT Solutions for Class-12 Biology Chapter-14 Ecosystem
(a) Plants are called as ___ because they fix carbon dioxide.
(b) In an ecosystem dominated by trees, the pyramid (of numbers) is ___ type.
(c) In aquatic ecosystem, the limiting factor for the productivity is ___
(d) Common detritivores in our ecosystem are ____
(e) The major reservoir of carbon on earth is ___
Solution:
(a) producers
(b) inverted or spindle
(c) light
(d) saprotrophs
(e) oceans
Question 2. Which one of the following has the largest population in a food chain?
(a) Producers
(b) Primary consumers
(c) Secondary consumers
(d) Decomposer’s
Solution:
(d) decomposer’s
Question 3. The second trophic level in a lake is
(a) phytoplankton
(b) zooplankton
(c) benthos
(d) fishes.
Solution:
(b) zooplankton
Question 4. Secondary producers are
(a) herbivores
(b) producers
(c) carnivores
(d) none of these
Solution:
(a) herbivores
Question 5. What is the percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), in the incident solar radiation.
(a) 100%
(b) 50%
(c) 1 – 5%
(d) 2 – 10%
Solution:
(b) 50%
Question 6. Distinguish between
(a) Grazing food chain and detritus food chain
(b) Upright and inverted pyramid
(c) Litter and detritus
(d) Production and decomposition
(e) Food chain and food web
(f) Primary and secondary productivity
Solution:
(a) Differences between grazing food chain and detritus food chain are as follows,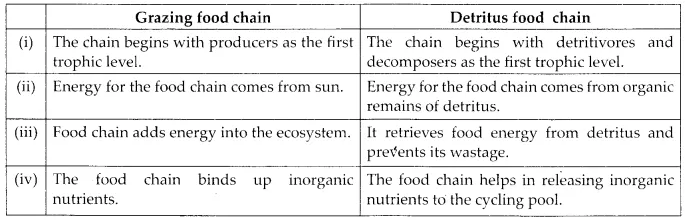
(b) Differences between upright and inverted pyramids are as follows,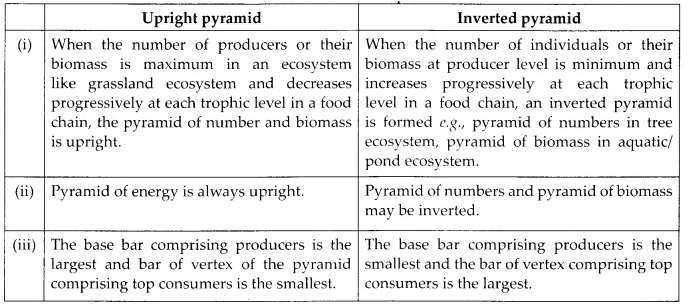
(c) Differences between litter and detritus are as follows,
(d) Differences between production and decomposition are as follows,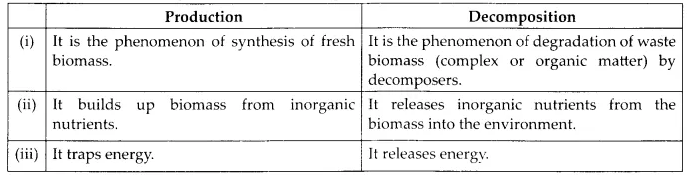
(e) Differences between food chain and food web are as follows,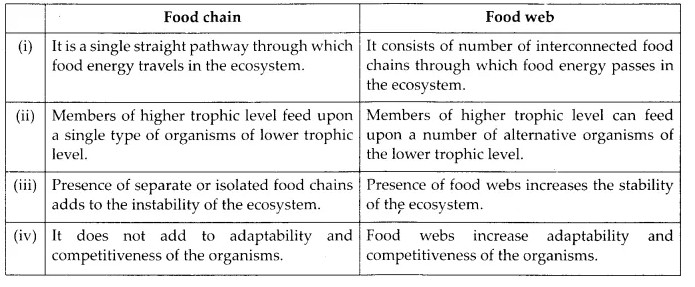
(f) Differences between primary productivity and secondary productivity are as follows,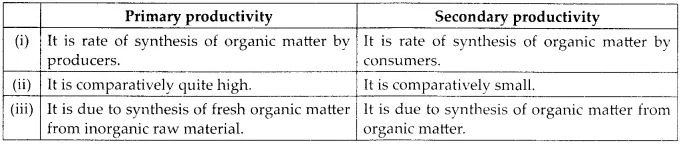
Solution:
Ecosystem: The system resulting from the interaction between organisms and their environment is called an ecosystem.
(a) Producers: Organisms, which can synthesize their own food are included under producers, e.g., Volvox, Pandorina, Oedogonium, Saggitaria, Utricularia, Azolla, Trapa, Lemna, Typha, Nymphaea etc. form the producer class of the pond ecosystem.
(b) Consumers:
1. Primary consumer: Animals, which feed on producers are included in this category e.g., Daphnia, Cyclops, Paramoecium, Amoeba, and small fishes.
2. Secondary consumers: Primary consumers also serve as food for water snakes, a few tortoises, few types of fish, etc. hence, these are carnivores.
3. Tertiary consumers: Secondary consumers also serve as food for aquatic birds like kingfishers, cranes, big fish and these together form a top-class carnivorous group and called tertiary consumers.
(c) Decomposers: All producers and consumers die and accumulate on the floor of the pond. Even the waste material and feces of these animals get accumulated on the floor of the pond. Similarly, the floor of the pond is also occupied by decomposers, which include bacteria and fungi. These decomposers decompose complex organic compounds of then- bodies into simpler forms which are finally mixed with the soil of the floor of ponds. These are again absorbed by the roots of producer plants and thus matter is recycled.
Solution: An ecological pyramid is a graphic representation of an ecological parameter, as a number of individuals present in various trophic levels of a food chain with producers forming the base and top carnivores the tip. Ecological pyramids were developed by Charles Elton (1927) and are, therefore, also called Eltonian pyramids.
There are three types of ecological pyramids, namely,
1. Pyramid of numbers
2. Pyramid of biomass
3. Pyramid of energy
Pyramid of numbers: It is a graphic representation of the number of individuals per unit area of various trophic levels stepwise with producers at the base and top carnivores at the tip. In a grassland, the producers, which are mainly grasses, are always maximum in number. This number then shows a decrease towards the apex, as the primary consumers (herbivores) like rabbits, mice, etc. are lesser in number than the grasses; the secondary consumers, snakes, and lizards are lesser in number than the rabbits and mice. Finally, the top (tertiary) consumers hawks or other birds, are the least in number. Thus, the pyramid becomes upright.
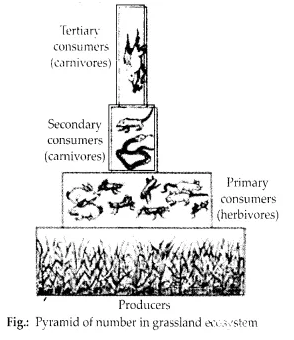
Pyramid of biomass: The amount of living organic matter (fresh and dry weight) is called biomass. Here, different trophic level of the ecosystem are arranged according to the biomass of the organisms. In grassland and forest, there is generally a gradual decrease in biomass of organisms at successive levels from the producers to the top carnivores. Thus these pyramids are upright. But in pond ecosystem, it is inverted because the biomass gradually increases from the producers to carnivores.
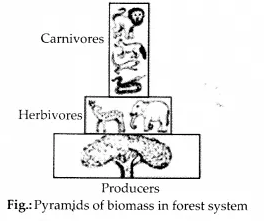
Solution: The rate of biomass production is called productivity.
It is expressed in terms of g-2yr-1 or(Kcal-m-2) yr-1 to compare the productivity of ecosystems.
It can be divided into Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) and Net Primary Productivity (NFP).
Gross Primary Productivity of an ecosystem is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. A considerable amount of GPP is utilized by plants in respiration.
Gross primary productivity minus respiration losses (R), is the Net Primary Productivity (NPP). GPP – R=NPP.
Primary productivity depends on:
(a) The plant species inhabiting a particular area.
(b) The environmental factors.
(c) Availability of nutrients.
(d) Photosynthetic capacity of plants.
Solution: Decomposition is the breakdown of dead or wastes organic matter by micro-organisms. Decomposition is both physical and chemical in nature. Processes involved in decomposition are – fragmentation, catabolism & leaching.
1. Fragmentation - The process primarily due to the action of detritus feeding invertebrate (detritivores) causes it to break into smaller particles. The detritus gets pulverized when passing through the digestive tracts of animals. Due to fragmentation, the surface area of detritus particles is greatly increased.
2. Catabolism - Enzyme degradation of detritus into simpler organic substances by bacteria and fungi.
3. Leaching - The process by which nutrients, chemicals, or contaminants are dissolved & carried away by water, or are moved into a lower layer of soil.
Various inorganic and organic substances are obtained by decomposition. Inorganic substances are obtained in the process of mineralization while organic substances are obtained in humification. A dark coloured amorphous substance called humus is formed by decomposition. Humus is highly resistant to microbial action & undergoes extremely slow decomposition. It serves as a reservoir of nutrients.
Solution: Ecosystems require a constant input of energy as every component of an ecosystem is regularly dissipating energy.
Two laws of thermodynamics govern this flow of energy. According to the first law of thermodynamics, energy can be transferred as well as transformed but is neither created nor destroyed. According to the second law of thermodynamics, every activity involving energy transformation is accompanied by the dissipation of energy. Except for deep hydrothermal ecosystems, the source of energy in all ecosystems is solar energy. 50% of the solar energy incident over the earth is present in PAR (photosynthetically active radiation).
Energy flow in an ecosystem is always unidirectional or one way, i.e., solar radiation → producers → herbivores → carnivores. It cannot pass in the reverse direction. There is a decrease in the content and flow of energy with the rise in trophic level. Only 10% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next.
Producer biomass (1000 K cal) → Herbivore biomass (100 K cal) → Carnivore I biomass (10 Kcal) Carnivore II biomass (1 Kcal)
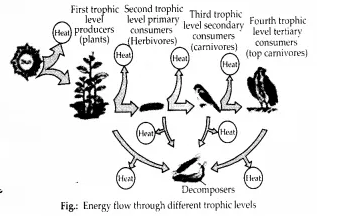
Question 12. Write important features of a sedimentary cycle in an ecosystem
Solution: Sedimentary Biogeochemical cycle:- It is the circulation of a biogeochemical between the biotic and abiotic compound of an ecosystem is a nongaseous being lithosphere or sediments of the earth. Sedimentary cycles occur in the case of phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, zinc, copper, etc.
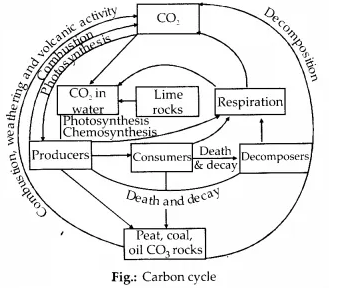
Solution: Carbon constitutes 49 percent of the dry weight of organisms and is next only to water. 71 percent of carbon is found dissolved in oceans. This ocean reservoir regulates the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Fossil fuels also represent a reservoir of carbon. Carbon cycling occurs through the atmosphere, ocean, and living and dead organisms. 4 x 1013 kg of carbon is fixed in the biosphere through photosynthesis annually.
A considerable amount of carbon returns to the atmosphere as Co2 through respiratory activities of the producers and consumers. Decomposers also contribute substantially to the CO2 pool by their processing of waste materials and dead organic matter of land or oceans. Some amount of fixed carbon is lost to sediments and removed from circulation. Burning of wood, forest fire and combustion of organic matter, fossil fuels, volcanic activity are additional sources for releasing Co2 into the atmosphere.
Human activities have significantly influenced the carbon cycle. Rapid deforestation and the massive burning of fossil fuels for energy and transport have significantly increased the rate of release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.

0 comment
Post a Comment