NCERT Solutions for Class-12 Physics Chapter-13 Nuclei
Question 1. (a) Two stable isotopes of lithium
(b) Boron has two stable isotopes
Answer:
(a) Atomic weight of lithium
Question 2. The three stable isotopes of neon :
Answer: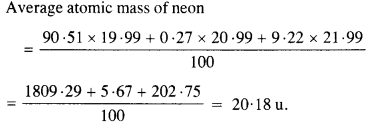
Question 3. Obtain the binding energy of a nitrogen nucleus (
mH = 1.00783 u
mn = 1.00867 u
mn = 14.00307 u
Give your answer in MeV.
Answer: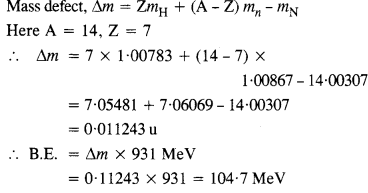
Question 4. Obtain the binding energy of the nuclei
in units of
mH =1007825u
mn =1008665u
m (
m (
Which nucleus has greater binding energy per nucleon?
Answer: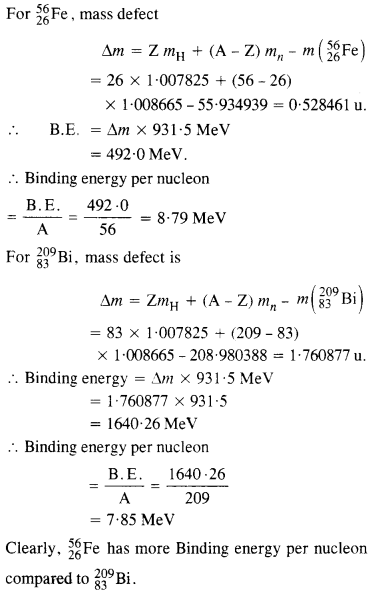
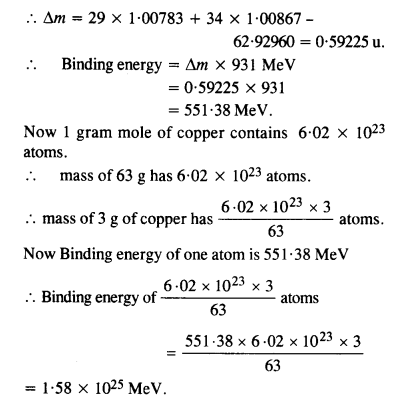
Question 5. A given coin has a mass of 3.0 g. Calculate the nuclear energy that would be required to separate all the neutrons and protons from each other. For simplicity assume that the coin is entirely made of
Answer: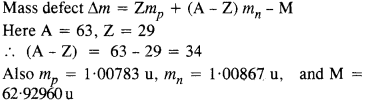
Question 6. Write nuclear equations for :
(a) the α-decay of
(b) the β–-decay of
(c) the β+-decay of
Answer: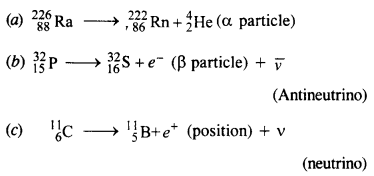
Question 7. A radioactive isotope has a half-life of T years. After how much time is its activity reduced to 3.125% of its original activity (b) 1% of original value ?
Answer: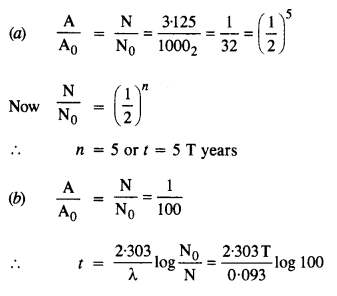
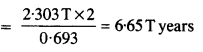
Question 8. The normal activity of living carbon-containing matter is found to be about 15 decays per minute for every gram of carbon. This activity arises from the small proportion of radioactive
Answer: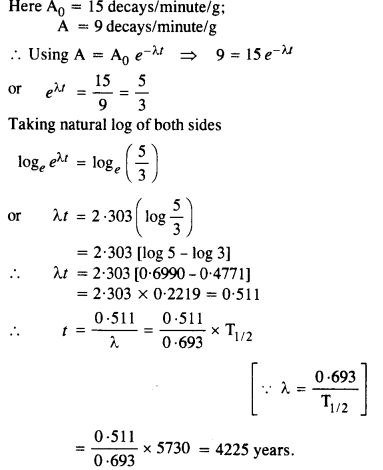
Half-life formula is the time required for the amount of something to fall to half its initial value.
Question 9. Obtain the amount of
Answer:
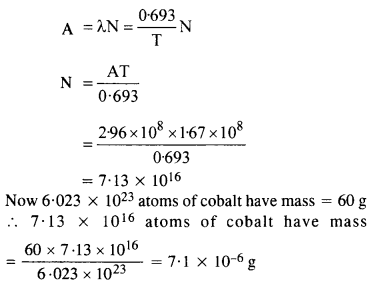
Question 10. The half-life of
Answer: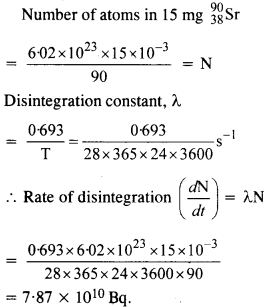
Question 11. Obtain approximately the ratio of the nuclear radii of the gold isotope
Answer: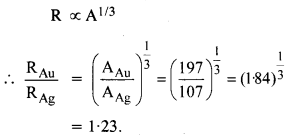
Question 12.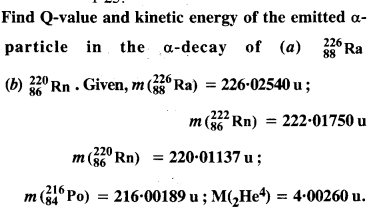
Answer:![]()

Question 13.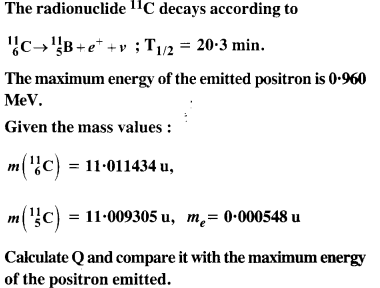
Answer: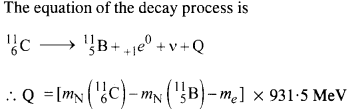
Here mN stands for the nuclear mass of the element or particle. In order to express the Q value in terms of the atomic masses, 6 me mass has to be subtracted from the atomic mass of 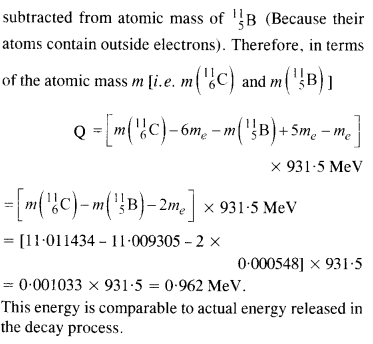
Question 14. The nucleus
m(
m(
Answer: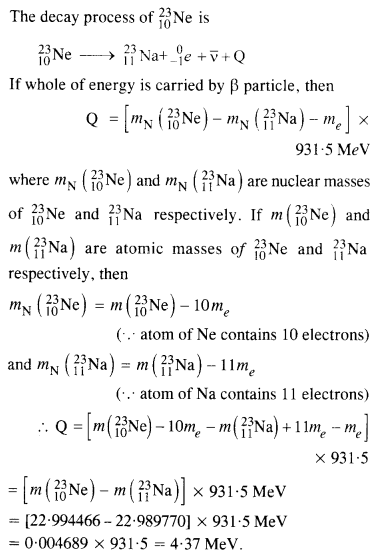
Question 15. The Q value of a nuclear reaction A + b ⇒ C + d is defined by [Q = mA + mb-mc– md] c2 where the masses refer to nuclear rest masses. Determine from the given data whether the following reactions are exothermic or endothermic.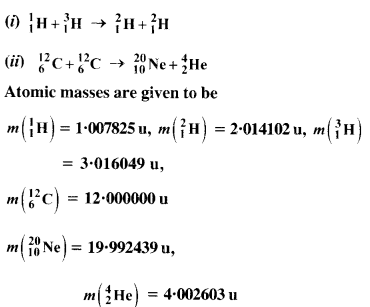
Answer: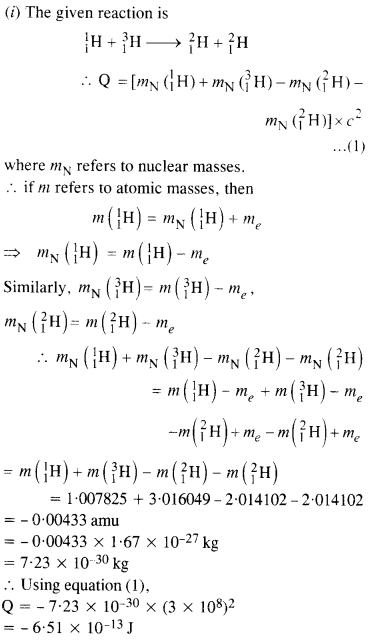

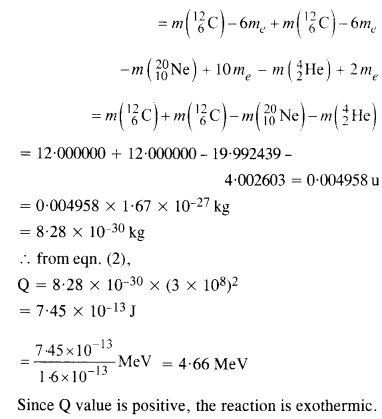
Question 16. Suppose, we think of fission of a
Answer:![]()

Question 17. The fission properties of
Answer: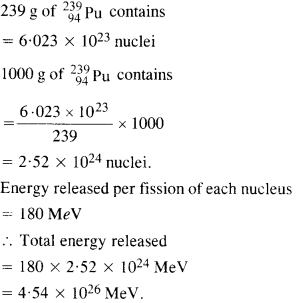
Question 18. A 1000 MW fission reactor consumes half of its fuel in 5.00 y. How much
Answer: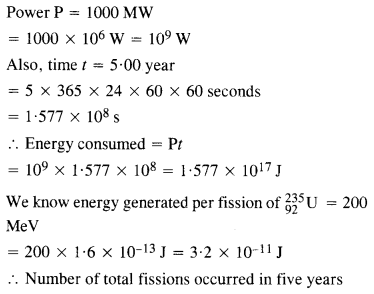
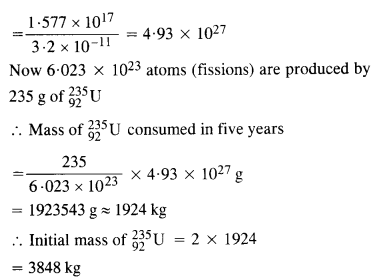
Question 19. How long an electric lamp of 100 W can be kept glowing by fusion of 2.0 kg of deuterium ? The fusion reaction can be taken as![]()
Answer: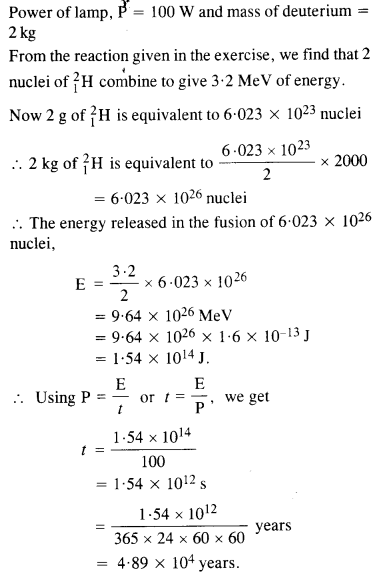
Question 20. Calculate the height of Coulomb barrier for the head on collision of two deuterons. The effective radius of deuteron can be taken to be 2.0 fm.
Answer: The initial mechanical energy E of the two deutrons before collision is given by
E = 2 K.E.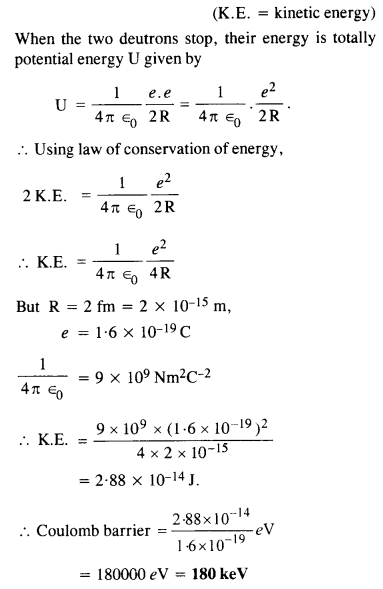
Question 21. From the relation R = R0 A1/3, where R0 is a constant and A is the mass number of a nucleus, show that nuclear matter density is nearly constant (i.e. independent of A)
Answer: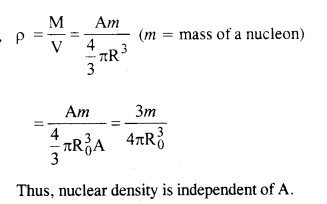
Question 22. For the β+ (positron) emission from a nucleus, there is another competing process known as electron capture (electron from an inner orbit, say, the K- shell, is captured by the nucleus and a neutrino is emitted).![]()
Show that if β+ emission is energetically allowed, electron capture is necessarily allowed but not vice-versa
Answer: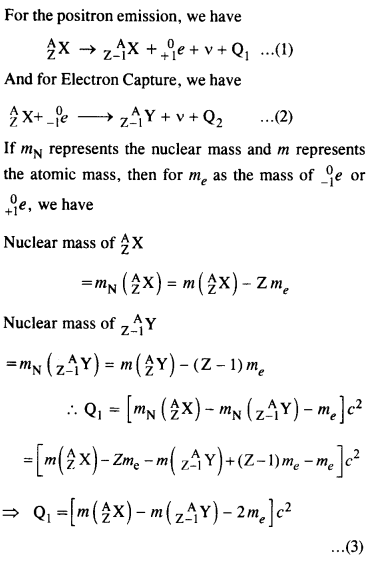
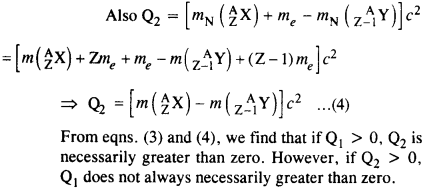
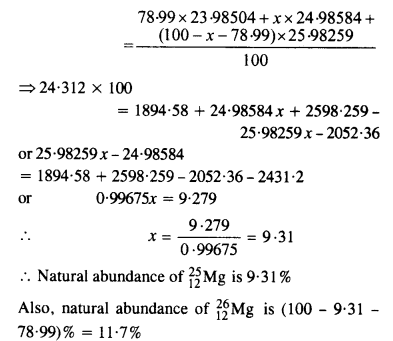
Question 23. In a Periodic Table the average atomic mass of magnesium is given as 24.312 u. The average value is based on their relative natural abundance on Earth. The three isotopes and their masses are
Answer: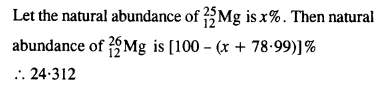
Question 24. The neutron separation energy is defined as the energy required to remove a neutron from the nucleus. Obtain the neutron separation energies of the nuclei 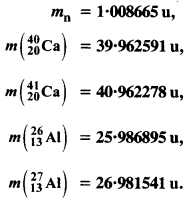
Answer:
Question 25.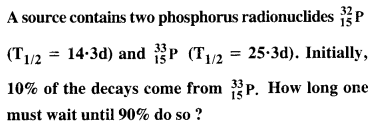
Answer:
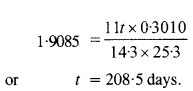
Question 26. Under certain circumstances, a nucleus can decay by emitting a particle more massive than an α-particle. Consider the following decay processes :![]()
(a) Calculate the Q values for these decays and determine that both are energetically possible.
(b) The Coulomb barrier height for α-particle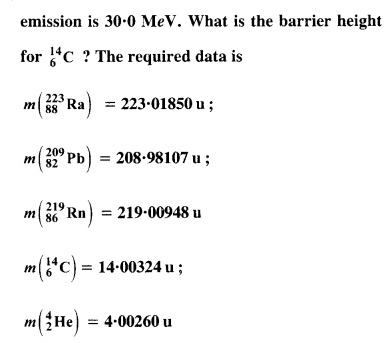
Answer:

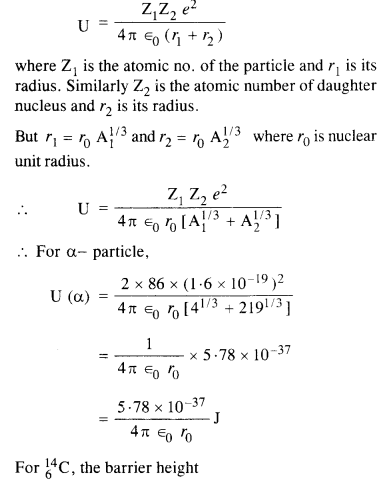
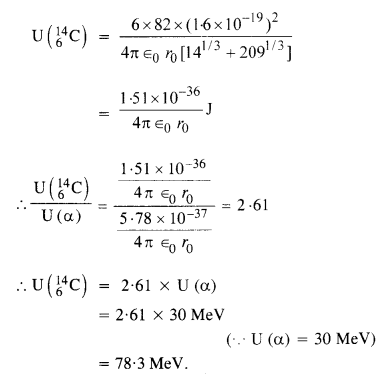
Question 27. Consider the fission of ![]()

Answer: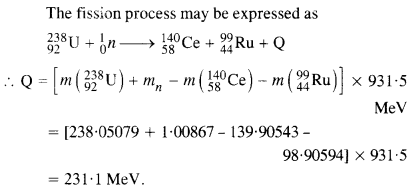
Question 28. Consider the D-T reaction (deuterium-tritium-fusion) given in eqn. :
(b) Consider the radius of both deuterium and tritium to be approximately 1.5 fm. What is the kinetic energy needed to overcome the Coulomb repulsion? To what temperature must the gases be heated to initiate the reaction?
Answer: From the equation given in the question,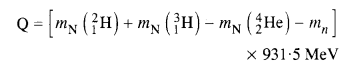
mN refers to the nuclear mass of the element given in the brackets and mn = mass of the neutron. If in represents the atomic mass, then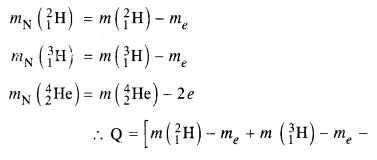

Question 29. Obtain the maximum kinetic energy of p-particles and the radiation frequencies to y decay in the following decay scheme. You are given that
m (198Au) = 197.968233 u
m (198Hg) = 197.966760 u
Answer: The total energy released for the transformation of 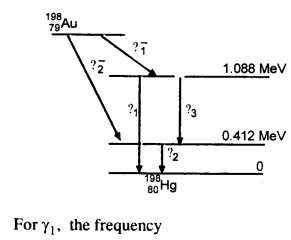

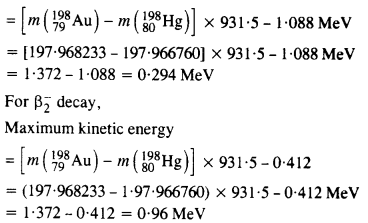
Question 30. Calculate and compare the energy released by (a) fusion of 1.0 kg of hydrogen deep within the sun and (b) the fission of 1.0 kg of 235U in a fission reactor.
Answer:
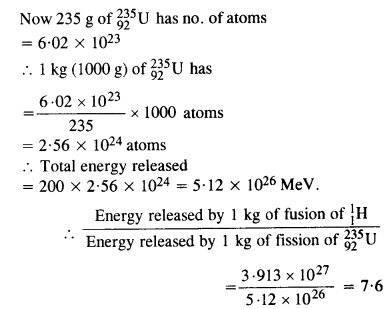
Question 31. Suppose India had a target of producing by 2020 AD, 200,000 MW of electric power, ten percent of which was to be obtained from nuclear power plant. Suppose we are given that, on average, the efficiency of utilisation (i.e., conversion to electric energy) of thermal energy produced in a reactor was 25%. How much amount of fissionable uranium did our country need per year by 2000 ? Take the heat energy per fission of 235U to be about 200 MeV. Avogadro’s number = 6.023 x 1023 mol-1.
Answer: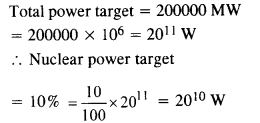

0 comment
Post a Comment