NCERT Solutions for Class-12 Biology Chapter-12 Biotechnology and Its Applications
NCERT EXERCISE
Question 1. Crystals of Bt toxin produced by some bacteria do not kill the bacteria themselves because
(a) bacteria are resistant to the toxin
(b) toxin is immature
(c) toxin is inactive
(d) bacteria encloses toxin in a special sac.
Solution:
(c) Toxin is inactive: In bacteria, the toxin is present in an inactive form called prototoxin. This gets converted into the active form when it enters the salivary gland of insects having an alkaline medium.
Solution: Transgenic bacteria are one that carries a transgene or a foreign gene of interest introduced using recombinant DNA technology. e. g., bacteria carrying the genes for human insulin.
In 1983, Eli Lilly an American company prepared two DNA sequences corresponding to A and B, chains of human insulin and introduced them in plasmids of E. coli to produce insulin chains. Chains A and B were produced separately, extracted and combined by creating disulfide bonds to form human insulin.
Solution:
Advantages of genetically modified crops or transgenic crops are as follows:
1. They are resistant to pests, herbicides and diseases.
2. They help to reduce post-harvest losses.
3. They enhance the nutritional value of food, e.g., a transgenic variety of rice (golden rice) is rich in vitamin A content.
4. Some transgenic plants, e.g., poplar trees are used to clean up heavy metal pollution from contaminated soil.
5. They are efficient in mineral usage and thus prevent early exhaustion of fertility of the soil.
Transgenic crops have several disadvantages also which are mentioned below:
1. Bt toxins expressed in pollen grains of transgenic crops are harmful for useful varieties of insects, e.g., honey bees and butterflies.
2. The foods produced by transgenic crops might cause toxicity and might result in allergies.
3. The bacteria present in human alimentary canal can become resistant to concerned antibiotic by taking up antibiotic resistance gene present in genetically modified food and become difficult to manage.
Question 4. What are Cry proteins? Name an organism that produces it. How has man exploited this protein to his benefit?
Solution: Cry proteins are a group of toxic protein which are highly poisonous to deficient types of insects. It is produced by a soil bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis. The genes controlling their formation are called cry genes eg:- Cry I Ab, Cry I Ac, Cry II Ab, The bacterium produces a protein in the crystal form of protoxin. Two cry genes have been incorporated in cotton (Bt cotton) while one has been introduced in corn (Bt corn) As a result Bt Cotton was disease resistant to bollworm and Bt corn was resistant to corn borer.
Question 5. What is gene therapy? Illustrate using the example of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
Solution: Gene therapy is the technique of genetic engineering used to replace a faulty gene with a normal, healthy functional gene. The first clinical gene therapy was given in 1990 to a 4 years old girl with adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA deficiency). This enzyme is very important for the immune system to function. Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) is caused due to a defect in the gene for the enzyme adenosine deaminase. SCID patient lacks functional T-lymphocytes and, therefore, fails to fight the infecting pathogens.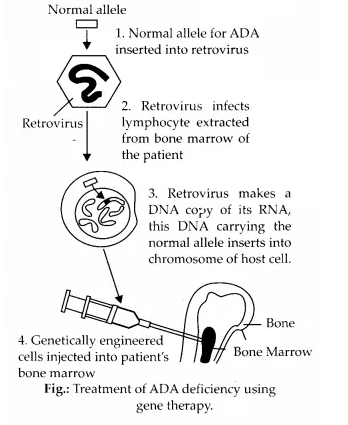
To perform gene therapy, lymphocytes are extracted from the patient’s bone marrow and a normal functional copy of human gene coding for ADA is introduced into these lymphocytes with the help of a retroviral vector. The cells so treated are reintroduced into the patient’s bone marrow. The lymphocytes produced by these cells contain functional ADA genes which reactivate the victim’s immune system. But, as these lymphocytes do not divide and are short-lived, so periodic infusion of genetically engineered lymphocytes is required. This problem can be overcome if stem cells are modified at an early embryonic stage.
Question 6. Diagrammatically represent the experimental steps in cloning and expressing a human gene (say the gene for growth hormone) into a bacterium like E.coli?
Solution: The given diagram represents the experimental steps in cloning and expressing a human gene for growth hormone into a bacterium E. coli.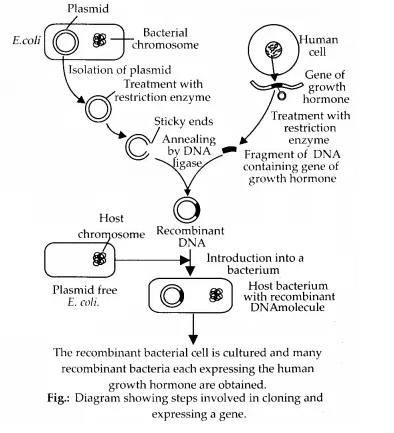
Solution: rDNA technology is a technique of genetic engineering that involves combining DNA from two different sources to produce recombined or recombinant DNA (rDNA). Oils are composed of glycerol and fatty acids. Thus, to produce oil-free seeds genes coding for glycerol or fatty acids should be identified and nucleotide sequences complementary to the sequence of these genes should be inserted adjacent to these genes in the early cells of the endosperm. During transcription, these complementary sequences will produce anti-sense RNAs to the RNAs produced by glycerol or fatty acids gene and will silence these genes. As a result, oil-free seeds will be produced.
Since glycerol is a common component of all the oils whereas various fatty acids combine with glycerol to form oils, thus it will be easier if we silence the gene for glycerol synthesis.
Question 8. Find out from the internet what is golden rice.
Solution: Golden rice is a GM rice with increased vitamin A content.
Question 9. Does our blood have proteases and nucleases?
Solution: Proteases occur naturally in all organisms. These enzymes are involved in a multitude of physiological reactions from simple digestion of food proteins to highly-regulated cascades (e.g., the blood-clotting cascade, the complement system, apoptotic pathways, and the invertebrate prophenoloxidase activating cascade). Proteases present in blood serum (thrombin, plasmin, Hageman factor, etc.) play important role in blood clotting, as well as in lysis of the clots, and the action of the immune system. Other proteases are present in leukocytes (elastase, cathepsin G) and play several different roles in metabolic control. Nucleases, such as deoxyribonucleases and ribonucleases are found in the blood which helps in the degradation of exogenous deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid circulating in the blood.
Question 10. Consult the internet and find out how to make orally active protein pharmaceuticals. What is the major problem to be encountered?
Solution: The problem is stomach enzymes and acids. Once you orally ingest a protein, the proteases in your stomach juices (trypsin, chymotrypsin, pepsin) will cleave the holy-hell out of your therapeutic protein and the acids will denature whatever’s left beyond all recognition. This is why proteins like insulin have to be injected.

0 comment
Post a Comment